Technology Custom Antibody Services
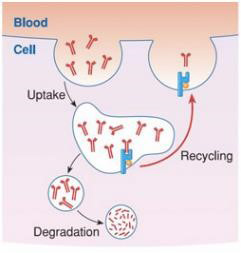
ImmunoGenes' patented technology platform IMG-AbS™, is an FcRn technology using genetically modified animals that overexpress the neonatal Fc Receptor (FcRn). Because of FcRn's role in antigen presentation, the company's animals are able to mount a strong immune response against weakly immunogenic targets.
Our recent studies have illustrated the advantageous effects of FcRn overexpression to significantly improve humoral immune response in the generation of antibodies, in principle, as biotherapeutics or in diagnostic assays.
IMG-AbS™ technology:
- Higher levels of circulating antibodies
- More efficient antigen presentation
- Higher antigen-specific immunoglobulin titers
- More diverse B cell repertoire
- Increased number of antigen-specific hybridomas
- Efficient humoral immune response against weakly immunogenic targets
- Production of antibodies against of highly conserved antigens - breaking immune tolerance
Intellectual Property:
- The IMG-AbS™ platform is protected by broad patent claims that have already been granted in Europe, Canada, Australia, Hong Kong, China and Japan.
- Our patent portfolio has been designed to protect the entire class of antibodies derived from the IMG-AbS™ platform. Each antibody arising from the platform will also be covered by individual composition of matter IP.
- We enjoy full freedom to operate under our patent coverage and till date have not granted exclusive licenses for IMG-AbS™ against any therapeutic target.
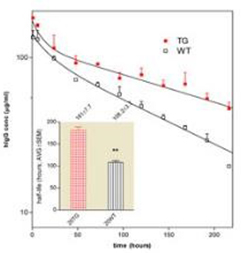
Higher levels of circulating antibodies
Pharmacokinetic analysis of the mouse and human IgGs in bFcRn transgenic (Tg) and wild type (wt) mice. Mean±SEM serum concentrations of injected mouse IgG and human IgG in Tg and wt mice; insert shows the half-life values of injected IgGs (Bender et al. 2007, Transgenic Research).
More efficient antigen presentation
|
bFcRn is strongly expressed in Tg dendritic cells and macrophages |
|
 |
 |
|
WESTERN BLOT |
qPCR |
Western blot analysis shows the expression of bovine α-chain protein in spleen (TgS), B cells (B) T cells (T), peritoneal neutrophil granulocytes (Ne), bone marrow derived dendritic cells (DC), and peritoneal macrophages (MΦ) from non-immunized bFcRn Tg animals. Based on its molecular weight, the 38-kDa band was specific for bFcRn as also evidenced by its expression in the bFcRn stable transfected cells (B4) for positive and spleen (WtS) from a control BALB/c mouse as negative control, respectively. Blot was stripped and rehybridized with an anti-β-actin monoclonal antibody as a loading control. qPCR analysis show expression ratios of the bFcRn to mFcRn at mRNA level in MΦ, DCs and spleen from bFcRn Tg mice analyzed with a quantitative real-time PCR assay. We found that the bFcRn expression was 3.8-, 2.6- and 10-fold higher compared to the expression of the mFcRn in spleen, MΦ, DCs, respectively (Vegh et al. 2012. PLoS One).
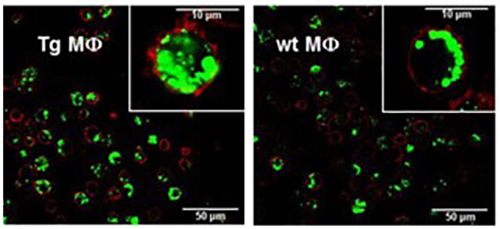
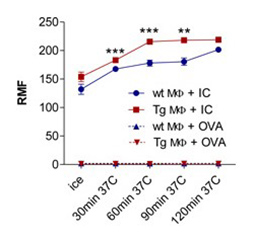
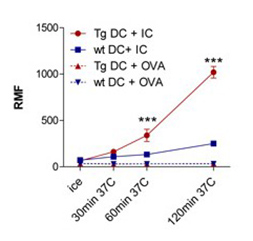
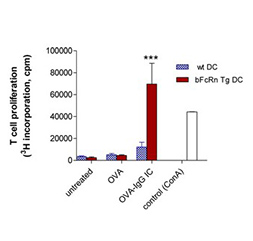
(A) Peritoneal macrophages (MΦ) and (B) bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (DCs) isolated from bFcRn Tg and wt mice were incubated with Alexa-conjugated ovalbumin(OVA)-IgG immune complex (IC) or with Alexa-conjugated OVA alone for the indicated times. The uptake was analyzed by flow cytometry. (A. cont) Peritoneal MΦ from bFcRn Tg and wt mice were incubated with Alexa-conjugated OVA-IgG (green) at 37°C for 60 min. Cells were then washed, and labeled with anti-CD11b (red) and visualized by confocal microscopy. (C) Bone marrow-derived DCs from wt and bFcRn Tg mice were left untreated or loaded with either OVA-IgG IC or OVA alone. CD4+ T cells from OVA TCR (DO11.10) Tg mice were then added to both the untreated and loaded DCs. After 24 hours, proliferating T cells were labeled for 12 h with [H3]-thymidine. As a positive control, CD4+ T cells were incubated with Concavalin A (ConA) (Vegh et al. 2012. PLoS One).
Higher antigen-specific immunoglobulin titers
|
FcRn overexpression results in increased antigen-specific IgM IgG and total IgG levels and number of antigen-specific B cells |
|||
 |
 |
 |
 |
| A | B | C | D |
Tg and wild-type mice were immunized with ovalbumin (OVA) (A) OVA-specific IgM and (B) OVA-specific IgG titers were nearly tripled in Tg mice compared with the wild-type (wt) animals. (C) Tg mice produced significantly higher amounts of total IgG compared to the wt mice. (D) Larger spleen and multiple-fold increase of OVA-specific IgM and IgG producer cells was detected in Tg mice compared with wt controls (Cervenak et al. 2011. The Journal of Immunology).
More diverse B cell repertoire
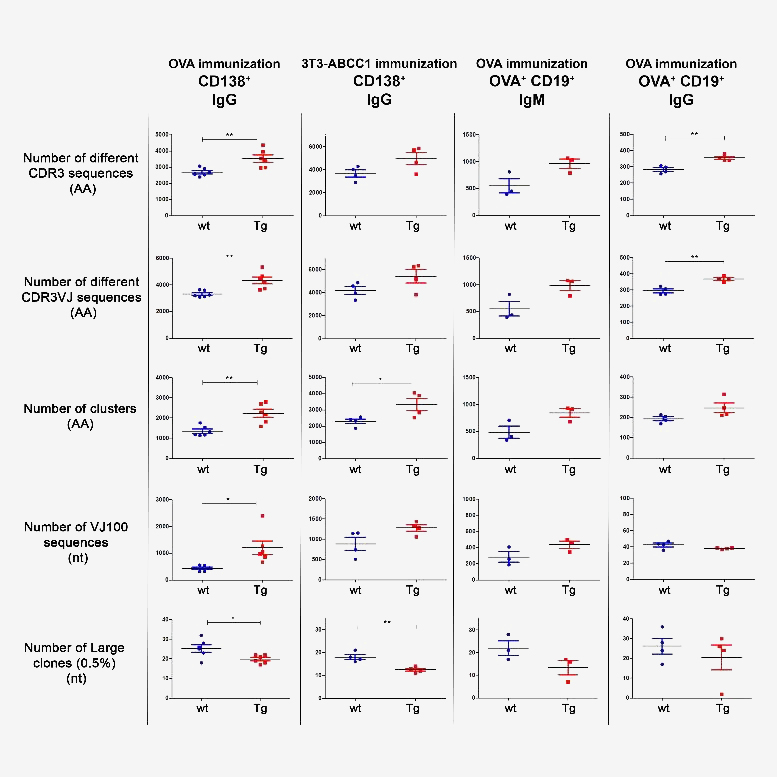
Next generation sequencing (NGS) analyses showed that in response to immunization with ovalbumin or transfected cells that expressed a unique membrane protein, our Tg animals developed a more diverse B cell repertoire than controls, which manifested in greater numbers of different clones, and clusters with fewer highly expanded large clones, as identified by the variable region (CDR3) of the immunoglobulin heavy chain. The increased antibody diversity in Tg mice after immunization was observed at both IgM and IgG levels, indicating that the increased humoral immune diversity in Tg mice is due to a higher number of both activated, antigen-specific naïve and isotype switched B cells.
Summary of diversity measures obtained from NGS analysis. The animals were immunized with OVA or cellular antigens and were sacrificed on day 24 or day 66. Different cell types (CD138+ or CD19+OVA+) were sorted and the Ig repertoires were analyzed by NGS. Results for different diversity measures are plotted in each row, with various immunization protocol, antigen, cell type and Ig isotype combinations represented in each column. Number of different CDR3 sequences (AA): Sequences with different CDR3 region at the amino acid level. Number of different CDR3VJ sequences (AA): Sequences with different CDR3 region at the amino acid level and with different V and J gene usage. Number of clusters (AA): Sequences that differ only in one amino acid in their CDR3 region were grouped into one cluster. Number of VJ100 sequences (nt): Different nucleotide sequences in the samples that did not contain any deviation from the germline sequence in the V and J genes. Number of large clones (0.5%) (nt): We considered a clone large if the proportion of its nucleotide sequences exceeded 0.5% of the repertoire. When a sample contains more dominant clones the diversity is lower as the distribution is less even. Horizontal black lines and colored error bars represent the mean ± SEM of the data. Individual points correspond to specific animals. Differences between mean values were tested using unpaired t-tests. Statistically significant results are marked with asterisks (*: p<0.05, **: p<0.01). (Szikora et al. 2020 Front. Immunol)
Increased number of antigen-specific hybridomas
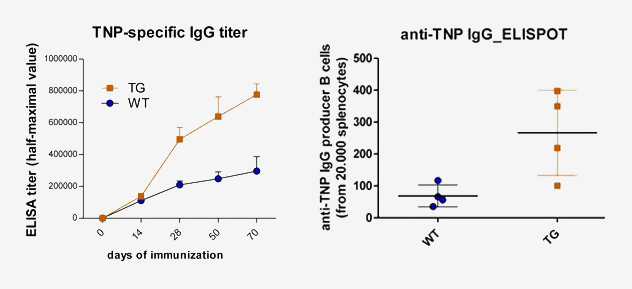
Immunization of bFcRn Tg mice with trinitrophenylated proteins generated a 3-5 fold increase in antigen-specific IgG titers and had significantly larger spleens containing higher number of antigen-specific B cells and plasma cells, analyzed by ELISA and ELISPOT assays as compare to their controls.
Fusion of the isolated splenocytes with standard mouse myeloma cells (SP2/0-Ag14) resulted in a 2-4 fold elevation of hybridization frequency for the hapten, or carrier-specific IgG positive microcultures, in Tg mice compared to controls (Schneider et al. 2011. Immunology Letters).
Efficient humoral immune response against weakly immunogenic targets

Cell populations in Tg and wt spleens 3 days after final booster immunization
Immunization with Influenza derived HA2-KLH elicits potent anti-peptide immune response only in bFcRn Tg mice
A) HA2-specific IgG titers showed a substantial increase in Tg mice compared to the negligible IgG titers of wild-type mice. (B) Absolute number of B cells, T cells, neutrophils, dendritic cells, and plasma cells were significantly higher in the spleen of transgenic animals as measured by FACS analysis (Vegh et al. 2011. mAbs).
Production of antibodies against of highly conserved antigens - breaking immune tolerance
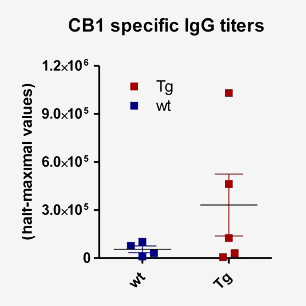
Immunization with highly conserved mouse cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1, GPCR) resulted in CB1 specific mAbs only in FcRn Tg mice (C-terminal mouse CB1 specific oligopeptide conjugated to KLH; this segment is identical to its human ortholog)
|
Mouse Type |
CB1 Positives Clones (IgG) |
|---|---|
|
Balb/c |
0 |
|
bFcRn Tg |
10 |